Eczema
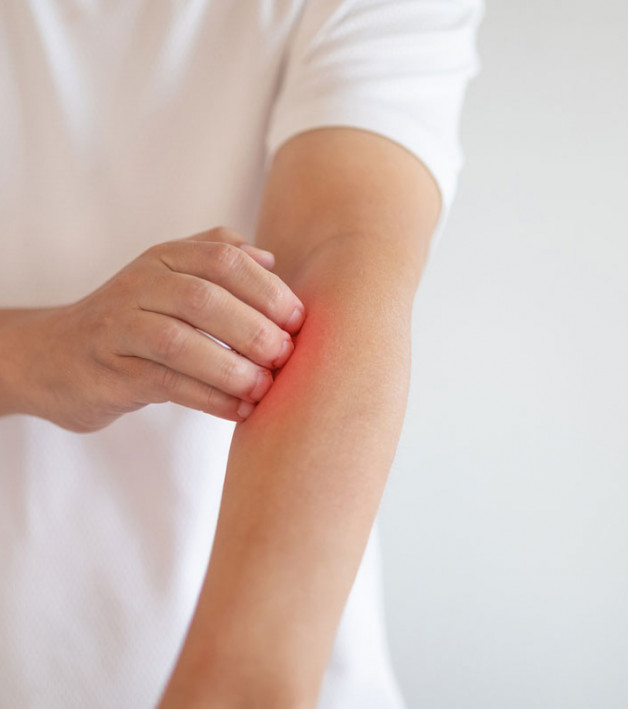
Although eczema may look different from person to person, it is most often characterized by dry, red, extremely itchy patches on the skin. Eczema is sometimes referred to as "the itch that rashes," since the itch, when scratched, results in the appearance of the rash.
Eczema can occur on just about any part of the body; however, in infants, eczema typically occurs on the forehead, cheeks, forearms, legs, scalp, and neck. In children and adults, eczema typically occurs on the face, neck, and the insides of the elbows, knees, and ankles. In some people, eczema may "bubble up" and ooze. In others, the condition may appear more scaly, dry, and red.
Chronic scratching causes the skin to take on a leathery texture because the skin thickens. One of the most important components of an eczema treatment routine is to prevent scratching. Because eczema is usually dry and itchy, the most common treatment is the application of lotions or creams to keep the skin as moist as possible. These treatments are generally most effective when applied directly after bathing (within three minutes is a common recommendation) so that the moisture from the bath is "locked in." Cold compresses applied directly to itchy skin can also help relieve itching. If the condition persists, worsens, or does not improve satisfactorily, another effective treatment is the application of nonprescription corticosteriod creams and ointments to reduce inflammation.